Hinode Microbubble Generator

(HMB): An Effective Aeration
Device for Wastewater Treatment System
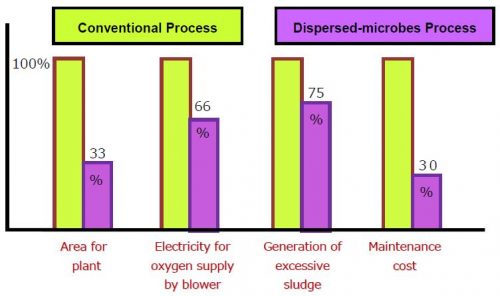
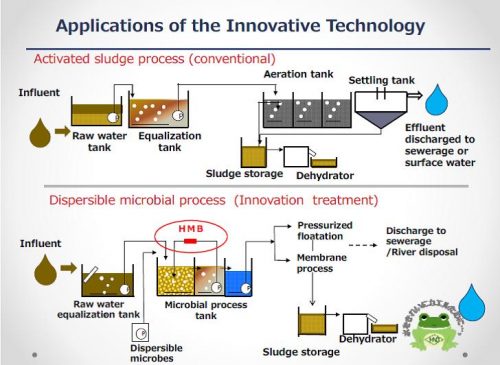
The activated sludge process today was invented more than 100 years ago. One of the major problems of the process is the dominance of filamentous microorganisms, which cause “bulking” of the sludge. Dispersed-Microbes Process invented by HINODE SANGYO Co., Ltd. is a revolutionary technology that prevents the “bulking.” The Dispersed-Microbes Process employs a device called Hinode Microbubble Generator (HMB). The device generates microbubbles by efficiently dissolving oxygen in the water to enhance the activity of aerobic microorganisms. It reduces generation of excessive sludge to 75% and ensures smooth processing of highly contaminated wastewater. Installation of the device is easy, and it is both cost and energy efficient.
Major Features and Advantages
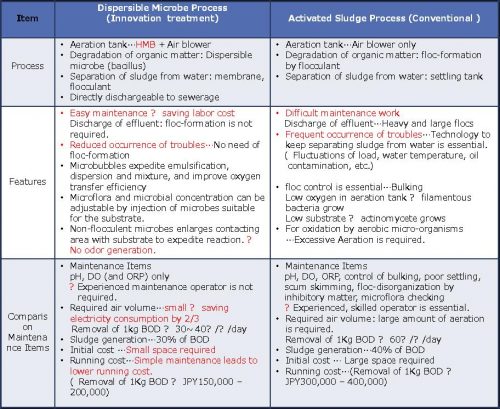
I. Easy Installation and Maintenance
Installation of HMB is simple and does not take a long time or a large space. The space required by Dispersed-Microbes Process is 33% of the space required by a conventional process. Maintenance is also easy, and it does not require an experienced operator. Special training for maintenance staff is not required.
II. Cost Efficiency
 HMB significantly reduces the operational cost without compromising the compliance to the environmental quality standards. While the operational cost of a conventional process is 300,000~400,000 JPY, that of Dispersed-Microbes Process is 150,000~200,000. Maintenance costs only 30~50%of the cost of a conventional process. The cost for chemical agents to treat problems can also be reduced to 1/3 because they will not be needed.
HMB significantly reduces the operational cost without compromising the compliance to the environmental quality standards. While the operational cost of a conventional process is 300,000~400,000 JPY, that of Dispersed-Microbes Process is 150,000~200,000. Maintenance costs only 30~50%of the cost of a conventional process. The cost for chemical agents to treat problems can also be reduced to 1/3 because they will not be needed.
III. Energy Efficiency
HMB greatly saves power consumption. The electricity used to operate Dispersed-Microbes Process is only 66% of the electricity used to operate a conventional process.
IV. Create More Jobs
 Installation of HMB involves a simple process. The HMB can be installed in many different sites. Therefore, it provides job opportunities to local people and contributes to the development of industrial sustainability.
Installation of HMB involves a simple process. The HMB can be installed in many different sites. Therefore, it provides job opportunities to local people and contributes to the development of industrial sustainability.
HMB is the best solution for wastewater treatment facilities in urban areas. One of the units has been installed in a factory located in the middle of a residential area, but the factory has never received a single complaint about foul odour or under-treated effluent from residents or city government over two years. HMB enhances the efficiency of wastewater treatment system and provides job opportunities to local people. Currently, five units of HMB are in operation, and five more units are in trial operation.
Technology Data
Technology data
Conceivable applications
“Dispersed-Microbes Process” invented by Hinode Sangyo is the revolutionary technology of the 21st century for wastewater treatment in place of well-established activated sludge process invented over 100 years ago.
A major problem in activated sludge process is occurrence of sludge “bulking” caused by the growth of filamentous microorganisms. Dispersed-Microbes Process intrinsically prevents sludge bulking, which ensures smooth processing of highly concentrated wastewater.
Hinode Sangyo’s Dispersed-Microbes Process remarkably enhances efficiency of wastewater treatment by activating aerobic microorganisms.
Dispersed-Microbes Process is the cutting-edge technology in terms of energy-saving, minimized use of wastewater treatment agents, ease of maintenance, minimized size of wastewater processing plant, complete elimination of foul smell, all of which have never been entirely achieved by other technologies in the history.
 Microbubble generator HMB (exhibition) Microbubble generator (on land)
Microbubble generator HMB (exhibition) Microbubble generator (on land)
Competitive advantage
Advantages of Hinode ’s Innovative Technologies
Three main points for cost reduction:
- Reduced amounts of agents such as bulking inhibitor & defoamers for treatment by 1/3
- Reduced electrical consumption by 1/3 by efficient operation of air blower
- Reduced maintenance time by 1/2
Achievements from use of Hinode technologies:
- Odor Suppression (fatty acid decay, methyl mercaptan and hydrogen sulfide gas)
- HMB can be easily installed in an existing plant.
- HMB’s strong mixing capability significantly raises the rate of dissolved oxygen generated by blowers. (160% rate increase measured by Hinode Sangyo)
- Hinode’s high-efficiency dispersible microbe process downsizes wastewater treatment.
Performance
- Space for the treatment plant can be minimized.
- Energy-saving by efficient operation of aeration blowers
- Reduced sludge generation
- Easy maintenance and low maintenance cost
Technical maturity
Supply record from 2013 to 2016:
1) Design and construction of a wastewater treatment plant embracing HMB and Dispersed-Microbes Process in a food-processing plant, and training of their maintenance staff.(*)
2) Five units of HMBs were sold and installed in existing wastewater treatment plants.
3) Ongoing trial operation of five units of HMBs in existing wastewater treatment plants.
(*) The food-processing factory supplies 100,000 lunch boxes and delicatessen foods to convenience stores a day. The factory operates 365 days a year and 24 hours a day.
Located in the middle of residence area, the factory has received no complaints from the residents for foul smell or undertreated effluent from both residents and city government for more than two years since the inauguration of Hinode Sangyo’s Dispersed-Microbes Process plant.
In addition, various costs, in particular, electricity bill has been remarkably reduced. Consequently, Hinode Sangyo’s Dispersed-Microbes Process has achieved superb “Customer Satisfaction.”
Conceivable risk
There is no conceivable risk.
Information on patent related to this technology
Patent No. 5574317
Patent No. 5728662
International Publication No. 2013/137010
Patent Application 2013-227636 under the PCT
Patent Application 2014-154253 under the PCT
Patent Application 2015-210210 (Waiting for publication)
Patent Application 2015-252285 (Waiting for publication)
Company Data
| Name | HINODE SANGYO Co., Ltd |
| Address | 3854 Ikebe-cho, Tsuzuki-ku, Yokohama City, Kanagawa 224-0053 Japan |
| Capital | JPY 20,000,000 |
| Contact person |
Ms. Kaori FUJITA |
| Number of employees | 11 |
| Date of company foundation | September 1976 |
| The type of business | Waste water treatment |
Modality of business transaction
Partnership
Hinode Sangyo would like to establish a partnership agreement with an existing company willing to learn and acquire their advanced technologies on wastewater treatment.
Starting from export (import) of Hinode’s products with technical assistance on how to provide maintenance services to local customers, we would like to transfer our know-how on how to design, construct and maintain Hinode’s epoch-making wastewater treatment plant, featuring high-efficiency treatment processes and low power, running and maintenance costs.
Export of product
Hinode Sangyo would like to export thier products directly from Japan to overseas customers. In the future, however, we would like to establish sales outlets or local subsidiaries.
Licensing of patent
Hinode Sangyo is willing to provide the license to execute their patented technologies to overseas companies who have sufficient capabilities and resources for utilizing their technologies.
Contact Person(s)
*Please mention that you saw UNIDO's website when making the first contact with the company.
Registered Category
- Environmental Technologies : Pollution Prevention and Control / Circular Economy (3R)