C-POWER Plant: Making Strides

in Waste Management
CR- POWER is a specialist in process design and engineering for waste-to-energy (WTE). The company has developed C-POWER plant to address these concerns. Because waste management is one of the largest issues in the developing world, there becomes a need to effectively deal with odor, water pollution and infestations that occur as a result. This negatively affects the health of the population. A new technology by CR-POWER allows factories that produce combustible waste to generate electricity from waste and cut down on disposal. This technology is easy to use, and turns wastes such as biomass and plastics into gas.
 Fig. 1 C-POWER Plant in Iwaki city, Japan (Copyright: CR-POWER LLC)
Fig. 1 C-POWER Plant in Iwaki city, Japan (Copyright: CR-POWER LLC)
Major Features and Advantages
Ⅰ. Easy to Use
Thanks to its streamlined design and ability to be used in a variety of areas, C-POWER Plant is easy to set up, use and maintain. There is no need for professionals with special qualification. It works by thermally decomposing organic carbon such as MSW (Municipal solid waste) and biomass to generate the fuel gas, rotate the engine, and generate electricity.
Ⅱ. Thermal Decomposition Rather Than Incineration
This technology allows waste to be thermally decomposed rather than incinerated, which results in the generation of fuel gas with a high caloric value. In the past, the only option to get rid of waste was to bury it or incinerate it. With thermochemical decomposition and gasification, this is no longer necessary.
Ⅲ. Unique Rotary Design
Thanks to a one of a kind rotary design: horizontal rorating cylinder, twice as much fuel gas generation can take place, when compared with standard pyrolysis technologies. This design (U-turn kiln and Hybrid kiln) allows for more than 80% energy recovery ratio.
Ⅳ. Utilization for Power Generation
Small-scale plants can use this gas for power generation. In addition, the fuel gas and hydrogen can be utilized for batteries and chemical supplies.
Ⅴ. No Harmful By-Products
This technology does not produce harmful by-products like nitrogen oxide or dioxin. As a result, there is no treatment process needed.
NEXCO East Japan is the first user of commercial plant in the country to use this technology. The hope for the future is that this technology can be used instead of incineration in developing countries.
Technology Data
Possible applications
Waste disposal and energy production
Waste: municipal solid waste (MSW), biomass, plastics and every kind of organic carbon.
Energy: electricity, fuel-gas and heat
Competitive advantage
Advantages
1. It does not reject any type and form of raw organic matter.
It can treat organic matter(s) such as kitchen garbage, wooden paper and plastic waste individually and all kinds as well. Also there is no need to standardize the form of waste matters.
2. High calorie gas can be obtained.
As there is no entry of the air, the generated gas does not contain nitrogen and becomes high calorie gas.
3. Easy operation
As the equipment works on normal pressure, it is not subject to the high pressure gas regulation law.
4. Electricity generation by compact plant is available.
As the power generation by incineration treats high pressure gas and the steam turbine only provides with low power generation efficiency, the profitability is difficult to achieve unless the volume of waste reaches 100 ton and over per day.
In the meantime, as C-POWER has a structure which gains revolution by the engine worked by the same normal pressure gas as the gas for the car, it is easy to handle with high efficiency. For these reasons, the profitability can be attained by the volume of waste of 10 ton per day.
5. Environmental burden is small.
As it works on thermal chemical reaction in non-oxidized environment, it does not generate harmful substance such as DXN, NOx and SOx.
Identification of competitive technology
Landfill & Incinerator
Power generation by steam
Performance
The electricity generating process based on current technologies is to incinerate MSW (municipal solid waste), generate high-pressure steam, rotate the turbine and generate electricity.
These technologies require:
a. MSW of 100 tons/biomass of 200tons or more a day
b. Dioxine treatment process
c. Qualified persons handling high-pressure gas
d. Lower steam temperature (leads to lower power generation efficiency below 20% for MSW of 100 tons)
Our technology called C-POWER* thermally decomposes organic carbon such as MSW, biomass etc. generates the fuel gas, rotates the engine, and generates electricity. This technology has the following advantages over the current technologies:
a. MSW of five tons a day is enough to operate plants
b. The Dioxine treatment process is unnecessary
c. A special qualification person is unnecessary
d. Higher power generation efficiency around 40%
*One of our recent technologies named Hybrid kiln includes “spiral small cylinder” in horizontal rotating cylinder which enables pyrolisis and steam reforming at the same time.
More than 80% energy recovery ratio (= Net produced gas energy / energy contained in organic carbon)
C-power plant operation with U-turn kiln can produce about 0.7 kWh/kg-df of electricity, and that with spiral-turn kiln can produce approximately 1.2 kWh/kg-df.
The residue rate is approximately 15% for U-turn kiln, and about 5% or less for spiral-turn kiln.
Conceivable risk
Fluctuation of waste collection should be carefully monitored.
Technical maturity / Past record of introduction
Development history of C-POWER
・2000 Invention of horizontal rotating cylindrical kiln (U-turn kiln) Inventor: Taizo Kunii (Professor emeritus of
University of Tokyo)
・2004 Design, production and experiment of pilot plant (20kg/h)
・2006 Design of test plant (200kg/h) Power generation 100kW
・2011 Design of commercial plant (tree waste 2,000t/year) Power generation 100kW
・2012 Invention of spiral cylinder interior horizontally rotating kiln (Hybrid kiln)
Inventor: Akimichi Hatta C-POWER LLC CEO
・2015 Design, production and experiment of hybrid kiln (2kg/h)
・2018 Design, production and experiment of hybrid kiln (20 kg/h)
Practically commercialized equipment (Commercial plant)
This plant was developed as a demonstration plant for pyrolysis gasification using biomass by 3 companies, i.e. CR-POWER LLC (Formerly OSTRAND Corp), Tekken Corporation and East Nippon Expressway Company Limited (NEXCO).
Such plant was an electricity generation plant by pyrolysis gasification using wastes of unnecessary grass and trees collected after the cutting and pruning of these which grow on the roadside during the maintenance process for the express way and the plant was installed in the rest area at Nasu-kogen of south bound Tohoku Express Way.
In March of 2014, 3-year-demonstration experiment was finished. Then its practicability was proven as biomass power generation plant.
Since May of 2015, the necessary modification and additional construction was conducted in order to use as commercial plant and it was brought into pilot operation in November and in March of the 2016, it was delivered to the NEXCO. After that the plant was put into a continuous operation as the commercial plant and NEXCO has been conducting pyrolysis power generation using wastes of grass and trees collected during the maintenance process for the express way. Under such circumstance, C-POWER (horizontally rotating cylindrical power generation plant) is a first commercial plant.
Information on patent related to this technology
N/A
Company Data
| Name | CR-POWER LLC |
| Address | 1F Place Canada 7-3-37, Akasaka, Minato-ku Tokyo, Japan |
| Capital | 25 million yen |
| Contact person |
Mr. Akimichi HATTA |
| Number of employees | 7 (1 for international operation) |
| Date of company foundation | 1st October, 2018 |
| The type of business | Process design for the plant to collect energy from the waste (WTE), Waste To Energy and in EPC, Engineering, Procurement and Construction. |
Modality of business transaction
Partnership
We arrange partnership in WTE business and WTE process engineering.
Attachments
Schematic illustration of technology
Business of C-POWER LLC
C-POWER* is a gasification power generation plant by a heat chemical reaction.
*C-POWER is an acronym of C of Carbon and POWER of Pyrolysis of Organic Waste to Energy & Resources and a trademark for pyrolysis gasification plant by CR-POWER.
The pyrolysis gasification plant which CR-POWER LLC developed using horizontal rotary kiln (Name: C-POWER) has pyrolysis capability per capacity 5 times and more when compared with the pyrolysis gasification plant of conventional rotary kiln. Therefore, the compact type of such plant can prove its high performance.
Also C-POWER has superiority in the respect that it can obtain 3 times as much high calorie gas as calorific value and it works regardless of type of fuel and form when compared with other pyrolysis gasification plant such as vertical kiln, rotating hearth kiln.
As C-POWER has large output of power generation and by its simple structure, the maintenance is easy and it can provide with profitability even when the plant is compact.
The factories, offices and small municipalities who entrusted their waste treatment to some companies can be benefitted in (1) stopping the waste treatment cost, (2) the cost reduction for the electricity and fuel by introducing C-POWER.
Characteristic of C-POWER
1. It features pyrolysis, not bio-decomposition.
As an energy use technology for combustible waste (organic), the power generation plant by incineration using combustion heat o organic waste is brought into practical use. While there is a technology which is put into use by using bio-decomposition of organic matter (decomposition by bacteria) to obtain fuel gas, C-POWER is a technology which obtains fuel gas by pyrolysis of organic matter.
2. It is not partial combustion pyrolysis but it is non-combustion pyrolysis.
In order to conduct pyrolysis of organic matter, the heat is necessary. The technology where the air (oxygen) is put into the pyrolysis equipment and that the pyrolysis is achieved by the heat derived from partial combustion of decomposed matter inside pyrolysis equipment is widely used. C-POWER works on non-combustion technology where the air is not put into the pyrolysis equipment and instead, the pyrolysis is achieved by the heat which is exerted from outside.
3. The style of C-POWER is not fixed bed, not fluidized but rotating filled bed.
The movement of solid organic matter in the pyrolysis equipment is categorized. One is fixed bed where the matter moves from top to the bottom according to the gravity. In the rotary kiln, the matter moves down in a slanted way while being rotated, otherwise, fluidized bed which makes matter afloat by the force of current is used but C-POWER is different from all of these and it is rotating filled bed style.
Technical description
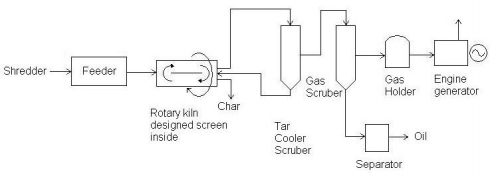
As shown in figure 1, our system of thermal decomposition for organic wastes consists of a hopper, feeder, rotary reactor, condenser, gas refiner, oil (gas) storage tank and dual fuel engine generator.
Specification of pyrolysis plant
| Plant capacity | 200 kg/h |
| Input (Raw materials) | Mixture of plastics (30.7%), biomass (60.8%) and others (8.5%) Bulk density 500 kg/m3 |
| Output (Products) | Gaseous products: 80 – 100 Nm3/h; 20,900 – 25,100 kJ/Nm3 ( Electricity 120kWh/h) Char 20 – 30 kg/h |
Development of C-POWER by Hybrid kiln
<Horizontal rotary kiln which conducts pyrolysis and reform of tar and char simultaneously: C-Power S>
C-POWER was completed as a pyrolysis gasification power generation plant but the tar (liquidized hydrocarbon compound) and char (solid hydrocarbon compound) which occur by pyrolysis simultaneously with gas need to be extracted from the kiln to be separately treated in a form of fuel. The gasification efficiency is about 50%.
The next subject is the development of high performance gasification equipment at gasification efficiency of 100% and more which enables (1) gasification of organic matter by pyrolysis at one equipment, (2) gasification of generated tar by pyrolysis, (3) gasification of char.
Gasification efficiency = obtained gas energy / organic energy input
As twice as much energy can be obtained by single equipment, the profitability can be maintained even by the compact plant. In this way, the organic carbon which is left behind by the factory and offices can be utilized at such place as a source of electricity and heat. Also by the waste incineration power generation, the extensive collection of the waste and their transportation become unnecessary. And then, it accelerates the prevention of global warming.
 Fig. 3 C-POWER U commercial plant (materlals: cut and pruned grass, and branches 5ton/day)
Fig. 3 C-POWER U commercial plant (materlals: cut and pruned grass, and branches 5ton/day)
 Fig.4 Engine generator 100kW (At the rest area of Nasu-Hyland in Tohoku Express Way, Japan)
Fig.4 Engine generator 100kW (At the rest area of Nasu-Hyland in Tohoku Express Way, Japan)
 Fig. 5 Experiment plant of horizontal rotating cylinder type S installed at The National Institute of Advanced Industrial
Fig. 5 Experiment plant of horizontal rotating cylinder type S installed at The National Institute of Advanced Industrial
Science and Technology (AIST) in Tsukuba city, Japan (Joint study by AIST and CR-POWER LLC)
 Fig. 6 Entire photo of S-turn kiln
Fig. 6 Entire photo of S-turn kiln
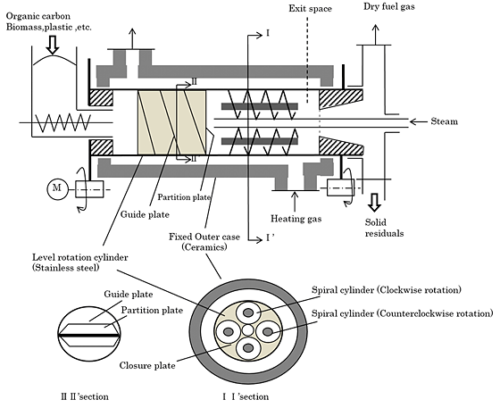
Fig. 7 The scheme of horizontal rotating cylinder
Typical operating results based on a pilot plant
1. Operation; Mixed plastics (Higher calorific value 9,519kcal/kg-dry base)
The components of mixed plastics used as feedstock and the typical operating results are shown in Tables 1 and 2 respectively. Operating conditions included a temperature of 700 degrees Celsius and feeding rate of 20 kg-plastics/h.
Table 1![]() Contents of three elements of mixed plastics
Contents of three elements of mixed plastics
| Moisture | Ash | Combustibles | Total | |
| wt% | 1.04 | 2.19 | 96.77 | 100 |
Table 2![]() Element of Combustibles (Dry base)
Element of Combustibles (Dry base)
| Ash | Combustibles | Elemental analysis | Total | |||||
| C | H | N | O | S | Cl | |||
| 2.21 | 97.79 | 73.8 | 12.9 | 1.11 | 9.86 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 100 |
Table 3![]() Output: Gas, Oil, Char (by pilot plant 20kg/hr)
Output: Gas, Oil, Char (by pilot plant 20kg/hr)
| wt% | Remarks notes | |
| Gas | 87.9 | Calorific value: 10.630kcal/Nm3 |
| Heavy tar | 5.8 | Boiling temp: >more than150℃ |
| Light tar | 4.6 (3.3*) | Boiling temp: 150-50℃ |
| Char | 1.7 | |
| Total | 100.0 |
*water content
2. Operation; Municipal solid waste
Dry MSW was heat resolved, and a combustible gas, the tar, and Char were obtained.
Table 4![]() Contents of municipal solid waste (original sample)*
Contents of municipal solid waste (original sample)*
| Water | Ash | Combustible | Total | |
| wt% | 45.8 | 5.6 | 48.6 | 100 |
*Higher calorific value 11,700 kJ/kg-wet base, 21,500 kJ/kg-dry base
Table 5![]() Contents of municipal solid waste prepared as RDF (dried sample)*
Contents of municipal solid waste prepared as RDF (dried sample)*
| Water | Ash | Combustible | Total | |
| wt% | 2.9 | 13.1 | 83.9 | 100 |
*Higher calorific value: 20,000 kJ/kg-dry base
Table 6![]() Elemental composition
Elemental composition
| Analytical results of six elements, (wt%) | Subtotal | Other | Total | |||||
| C | H | N | O | S | Cl | |||
| 44.7 | 6.7 | 0.9 | 31.9 | 0.0 | 2.6 | 86.9 | 13.1 | 100 |
*Higher calorific value: 20,000 kJ/kg-dry base
Table 7![]() Output : Gas, Oil, Char (by pilot plant 20kg/hr)
Output : Gas, Oil, Char (by pilot plant 20kg/hr)
| wt% | Remarks notes | |
| Gas | 52.5 | 23800 kJ/Nm3 |
| Heavy tar | 2.8 | |
| Light tar | 29.1 (14.9*) | |
| Char | 15.6 | Organic: 3.3, Inorg.: 12.3 |
| Total | 100 |
*Water content
Comparison between conventional furnace, U-turn and S-turn kiln
Table 8 Technical comparison between conventional furnace and CR-POWER’s facilities
| Conventional type | CR-POWER | ||
| Vertical furnace | Type of rotation cylinder | ||
| U-turn kiln | Spiral-turn kiln | ||
| Acceptable waste | Piece of wood (improper plastics) |
Various combustibles (plastics, garbage, paper, wood etc.) |
|
| Heat supply | Partial combustion | Heat transfer | |
| Fuel gas electricity obtained | Usual 0.5kWh/kg-df |
Slightly large 0.7kWh/kg-df |
Quite large 1.2kWh/kg-df |
| Quantity of residual | 5% or less | About 15% | 5% or less |
| Case of operation | Every country | Japan: Highway Nasu-Kogen service area | Japan: P-company commissioned from NEDO |
Contact Person(s)
*Please mention that you saw UNIDO's website when making the first contact with the company.
Registered Category
- Energy Technologies : Renewable energy
- Environmental Technologies : Circular Economy (3R)